What is Stack?
A stack is a linear data structure that stores a collection of objects. The stack operations follow the First In Last Out ( FILO ) order. The Stack contains only one pointer called top pointing to the topmost element in the stack. And the operations in a stack are performed only from one end or The insertion or deletion of elements in a Stack can be performed only from one end.
 |
| six stacks of books |
Stack Array Implementation Using C++:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_SIZE 101
int A[MAX_SIZE];
int top = -1;
void print(){
int i;
cout<<"Stack: ";
for(i=0;i<=top;i++){
cout<<A[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<"\n";
}
void push(int x){
if(top==MAX_SIZE-1){
cout<<"Error: stack overflow\n";
}
A[++top]=x;
print();
}
void pop(){
if(top==-1){
cout<<"Error NO element to pop";
return;
}
top--;
print();
}
int Top(){
return A[top];
}
int main()
{
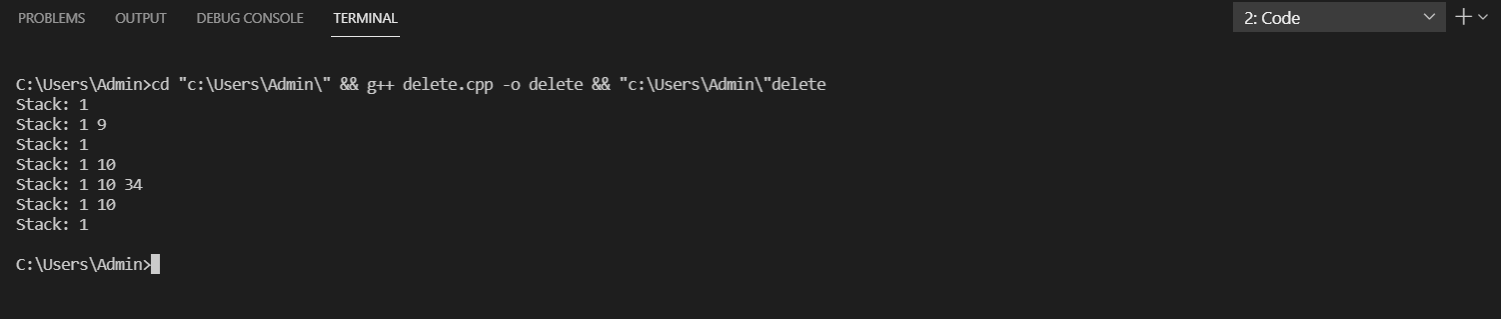
push(1);
push(9);
pop();
push(10);
push(34);
pop();
pop();
return 0;
}
Output:
Stack Linked List Implementation Using C++:
// Stack Linked List Implementation Using C++
// Time Complexity of Push and Pop operations are O(1) as we are using head as top
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
Node *next;
};
Node *top = NULL;
void push(int x){
Node *temp = new Node();
temp->data=x;
temp->next= top;
top = temp;
}
void pop(){
Node *temp;
if(top==NULL) cout<<"Stack is Empty\n";
temp=top;
top=top->next;
free(temp);
}
void print(){
Node* temp = top;
while(temp!=NULL){
cout<<temp->data<<' ';
temp = temp->next;
}
cout<<"\n";
}
int main()
{
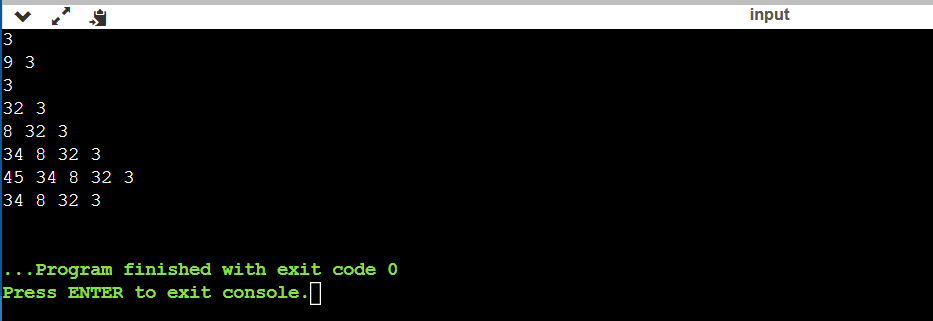
push(3);
print();
push(9);
print();
pop();
print();
push(32);
print();
push(8);
print();
push(34);
print();
push(45);
print();
pop();
print();
return 0;
}
Output:
String Reversal Using Stack In C++:
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(n)
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
void Reverse(char *C, int n){
stack<char> S;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
S.push(C[i]);
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
C[i]=S.top();
S.pop();
}
}
int main() {
char C[52];
cout<<"Enter a striing: ";
gets(C);
Reverse(C,strlen(C));
cout<<"output = "<<C;
}
Stack Reversal Using Linked List in C++:
#include <iostream>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
Node *next;
};
Node *top = NULL;
void Reverse() {
if(top==NULL) return;
stack<struct Node*> S;
Node* temp = top;
while(temp!=NULL){
S.push(temp);
temp=temp->next;
}
temp = S.top();
top = temp;
S.pop();
while(!S.empty()){
temp->next = S.top();
S.pop();
temp=temp->next;
}
temp->next=NULL;
}
void push(int x){
Node *temp = new Node();
temp->data=x;
temp->next= top;
top = temp;
}
void pop(){
Node *temp;
if(top==NULL) cout<<"Stack is Empty\n";
temp=top;
top=top->next;
free(temp);
}
void print(){
Node* temp = top;
while(temp!=NULL){
cout<<temp->data<<' ';
temp = temp->next;
}
cout<<"\n";
}
int main()
{
push(4);
push(3);
push(34);
push(84);
push(34);
push(43);
print();
Reverse();
print();
return 0;
}
Output:
C++ Program For Balanced Paranthesiss Checking:
//C++ program for balanced paranthesis checking
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool AreParanthesisBalanced(string x){
stack<char> s;
char c;
for(int i=0;i< x.length();i++){
if(x[i]== '(' || '{' || '['){
s.push(x[i]);
continue;
}
if(s.empty()){
return false;
}
switch(x[i]){
case ')' :
c = s.top();
s.pop();
if(c== '{' || '['){
return false;
}
break;
case '}':
c = s.top();
s.pop();
if(c== '(' || '['){
return false;
}
break;
case ']':
c = s.top();
s.pop();
if(c== '{' || '('){
return false;
}
break;
}
}
return(s.empty());
}
int main()
{
string x = "{)";
if (AreParanthesisBalanced(x)){
cout << "Balanced";
}
else {
cout << "Not Balanced";
}
return 0;
}
Stack List Implementation Using Python:
class ArrayStack:
def __init__(self):
self.data=[]
def len(self):
return len(self.data)
def is_empty(self):
return len(self.data)==0
def push(self, x):
self.data.append(x)
def pop(self):
if self.is_empty():
print("No elements to pop")
return self.data.pop()
def top(self):
if self.is_empty():
print("Stack is empty")
return self.data[-1]
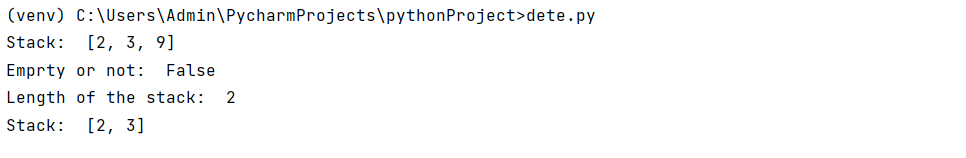
stack1 = ArrayStack()
stack1.push(2)
stack1.push(3)
stack1.push(9)
print("Stack: ",stack1.data)
print("Emprty or not: ",stack1.is_empty())
stack1.pop()
print("Length of the stack: ",stack1.len())
print("Stack: ",stack1.data)
Output:
Stack Singly Linked List Implementation Using Python:
class Node:
def __init__(self, data, next):
self.data = data
self.next = next
class Stack:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def is_empty(self):
return self.head == None
def push(self, data):
if self.head == None:
self.head = Node(data,None)
else:
nnode = Node(data, self.head)
self.head = nnode
def pop(self):
if self.head == None:
return None
else:
temp = self.head
self.head = self.head.next
temp.next = None
return temp.data
def print(self):
temp = self.head
if self.head == None:
print("Stack is empty")
else:
while temp!=None:
print(temp.data,end=' ')
temp = temp.next
return
stk = Stack()
stk.push(3)
stk.push(9)
stk.push(4)
stk.push(4)
stk.print()
stk.pop()
stk.pop()
print('\n')
stk.print()
Output:







0 Comments